Python_数据容器¶
数据容器:列表(List)、元组(Tuple)、字典(Dictionary)、集合(Set)¶

列表list:有序可变集合¶
-
tip:列表可以一次存贮多个数据,且可以为不同的数据类型,支持嵌套¶
定义列表:¶
| Python | |
|---|---|
定义空列表:¶
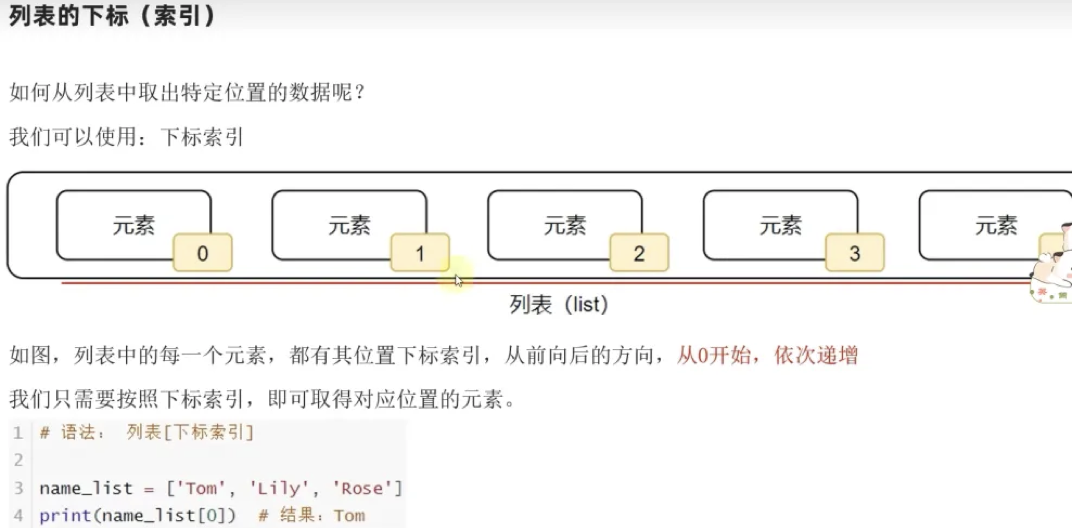
列表的下标:¶

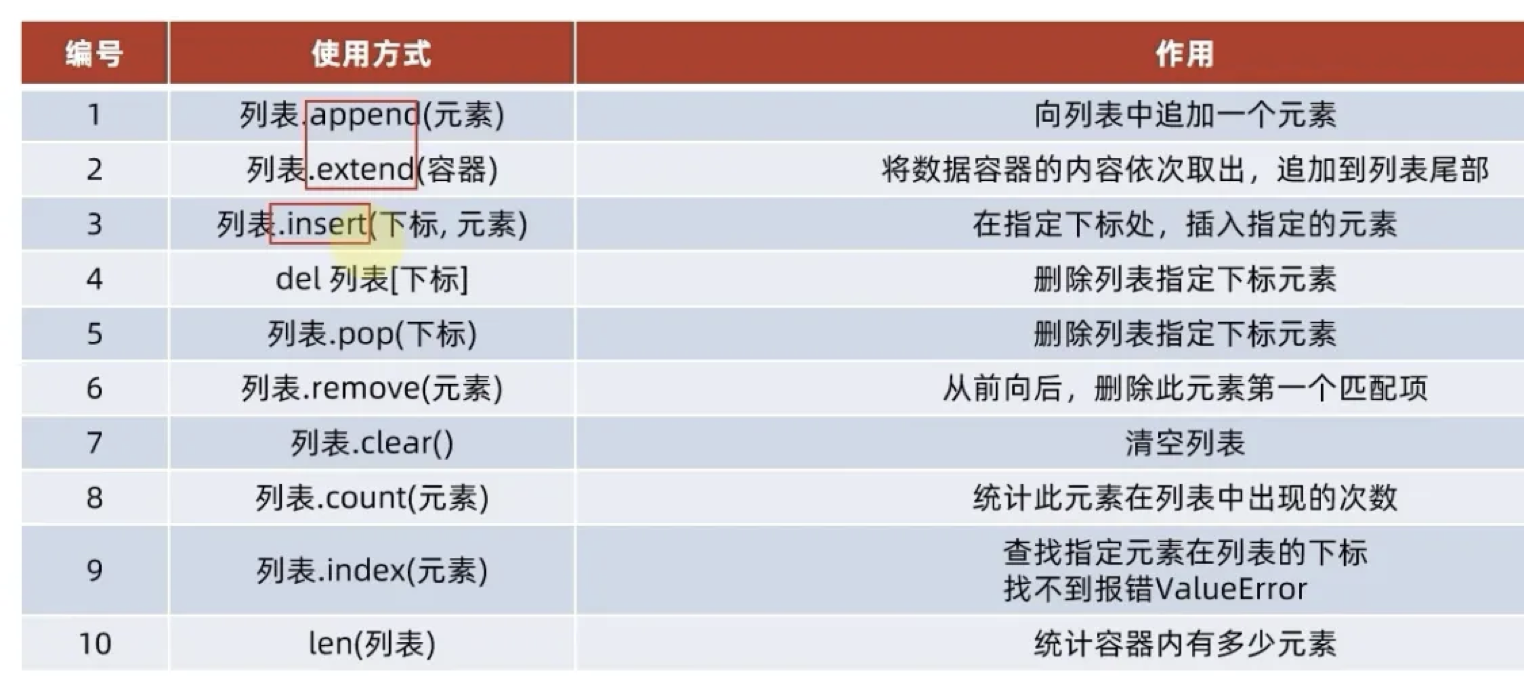
列表常用操作:¶
For\while 循环遍历列表:¶
| Python | |
|---|---|
元组tuple:不可以修改的list¶
元组定义:¶
| Python | |
|---|---|
定义空元组:¶
元组操作:与列表操作几乎一致,不过操作较少¶

元组的遍历:同列表¶
| Python | |
|---|---|
字典dict:¶
- 由两部分组成,一般通过字key 找到信息值value
- 字典的key是不能重复的 如果出现重复的情况的话 后面的会覆盖前面的

字典的定义:¶
| Python | |
|---|---|

字典的使用与循环:¶
集合set:¶
- 最主要的特点就是不支持元素重复 一般用来去重 但是他的内容和前面的地方不一样的点在于其无序性的特点
- 定义空集合一定是 set() 因为{} 是空字典
基本语法:¶

集合操作:¶
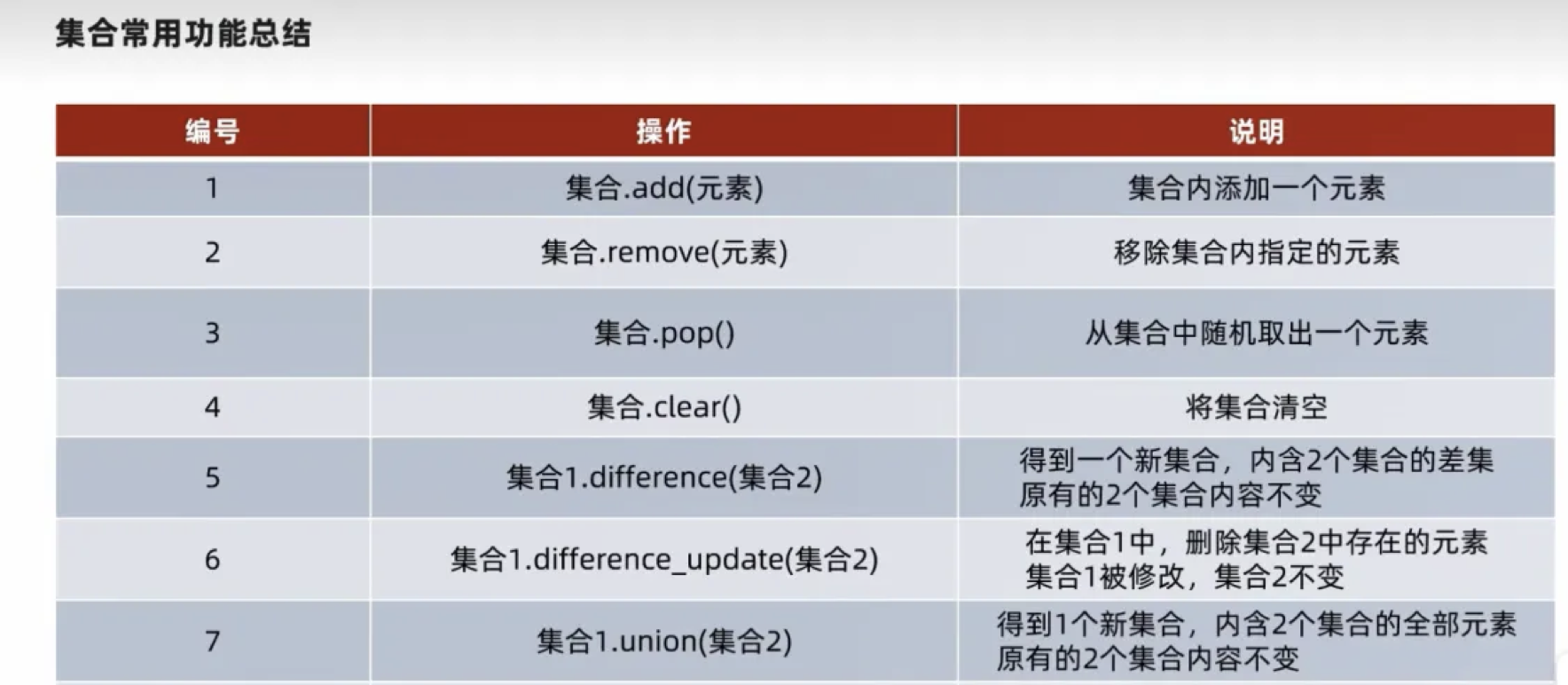
集合运算:高中内容¶
-
交集(Intersection):返回两个集合中都包含的元素,即它们的公共元素。格式:set1 & set2 或 set1.intersection(set2)
-
并集(Union):并集运算会返回两个集合的所有元素,但不会重复,包含两者中的所有唯一元素。格式:set1 | set2 或 set1.union(set2)
-
差集(Difference):差集运算会返回存在于第一个集合但不存在于第二个集合中的元素。格式:set1 - set2 或 set1.difference(set2)